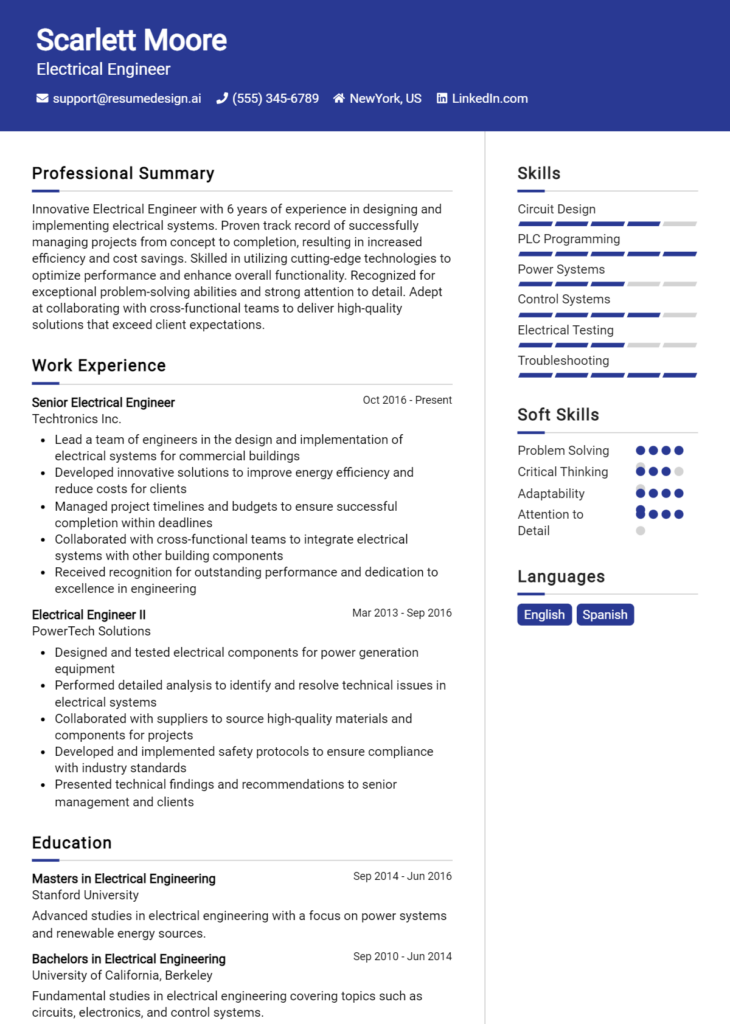
Semiconductor Engineer Core Responsibilities
A Semiconductor Engineer plays a crucial role in designing, developing, and testing semiconductor devices and systems, acting as a bridge between engineering, manufacturing, and quality assurance departments. This role requires a strong foundation in electrical engineering principles, analytical problem-solving skills, and proficiency in simulation software. By effectively collaborating across functions, Semiconductor Engineers contribute to the organization’s overall goals, ensuring product performance and reliability. A well-structured resume that highlights these technical and operational abilities can significantly enhance job prospects.
Common Responsibilities Listed on Semiconductor Engineer Resume
- Design and develop integrated circuits and semiconductor devices.
- Conduct simulations and performance analyses to optimize device functionality.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams for product development and testing.
- Oversee the fabrication process and troubleshoot manufacturing issues.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
- Perform failure analysis and reliability testing on semiconductor products.
- Document designs, test results, and operational procedures.
- Evaluate and select materials for semiconductor applications.
- Stay updated on emerging technologies and trends in semiconductor engineering.
- Provide technical support and training to manufacturing personnel.
High-Level Resume Tips for Semiconductor Engineer Professionals
In the competitive field of semiconductor engineering, a well-crafted resume is essential for making a strong first impression on potential employers. Your resume serves as the initial gateway to showcase your technical expertise, relevant experience, and unique achievements in this specialized industry. It’s crucial that it accurately reflects your skills and accomplishments, as hiring managers often sift through numerous applications in search of the right candidate. This guide aims to provide practical and actionable resume tips specifically tailored for Semiconductor Engineer professionals, helping you stand out in a crowded job market.
Top Resume Tips for Semiconductor Engineer Professionals
- Tailor your resume to each job description by incorporating keywords and phrases that reflect the specific requirements and responsibilities of the position.
- Highlight your relevant experience, focusing on projects and roles that directly relate to semiconductor design, fabrication, and testing.
- Quantify your achievements by including metrics such as yield improvements, cost reductions, or performance enhancements to demonstrate the impact of your work.
- Showcase your technical skills prominently, including proficiency in software tools, programming languages, and methodologies relevant to semiconductor engineering.
- Include any certifications or specialized training that may give you an edge, such as Six Sigma, Lean Manufacturing, or specific semiconductor processes.
- Use a clean and professional format, ensuring that your resume is easy to read and visually appealing to capture the attention of hiring managers.
- Incorporate a summary statement at the top of your resume that encapsulates your expertise and career goals, making it easy for employers to understand your value proposition.
- List publications or patents if applicable, as these can significantly enhance your credibility and showcase your contributions to the field.
- Keep your resume concise, ideally one page, focusing on the most relevant information to prevent overwhelming the reader.
By implementing these tips, you can significantly enhance your chances of landing a job in the Semiconductor Engineer field. A well-structured and targeted resume not only showcases your qualifications but also demonstrates your understanding of the industry’s demands, making you a compelling candidate for potential employers.
Why Resume Headlines & Titles are Important for Semiconductor Engineer
In the competitive field of semiconductor engineering, a well-crafted resume headline or title serves as a crucial first impression that can determine whether a hiring manager takes a closer look at your qualifications. A strong headline is concise yet powerful, summarizing a candidate's key qualifications in one impactful phrase. It should be directly relevant to the position being applied for, immediately grabbing the attention of recruiters and conveying the candidate's unique value proposition. An effective resume headline not only highlights pertinent skills and experiences but also sets the tone for the rest of the resume, making it essential for candidates looking to stand out in a technical and specialized industry.
Best Practices for Crafting Resume Headlines for Semiconductor Engineer
- Be concise: Aim for one impactful phrase that encapsulates your expertise.
- Be specific: Tailor the headline to reflect the specific role you are applying for.
- Highlight key strengths: Include your most relevant skills or accomplishments.
- Use industry keywords: Incorporate terms commonly recognized in semiconductor engineering.
- Showcase your experience: Reference years of experience or specialized knowledge.
- Make it impactful: Use dynamic verbs or action-oriented language to convey energy.
- Avoid jargon: Ensure clarity and avoid overly technical terms that may confuse recruiters.
- Match the job description: Align your headline with the requirements outlined in the job posting.
Example Resume Headlines for Semiconductor Engineer
Strong Resume Headlines
Innovative Semiconductor Engineer with 5+ Years in Advanced Chip Design
Experienced RF Engineer Specializing in High-Frequency Circuit Design
Results-Driven Semiconductor Expert with Proven Success in Process Optimization
Detail-Oriented Engineer with Expertise in VLSI Design and Test Development
Weak Resume Headlines
Engineer Seeking Opportunities
Looking for a Job in Semiconductors
Strong resume headlines are effective because they provide a clear and compelling summary of the candidate's qualifications, making it easy for hiring managers to quickly gauge their fit for the role. They utilize specific language and industry-relevant keywords to resonate with recruiters, while also showcasing the candidate's unique achievements. Conversely, weak headlines fail to impress because they lack specificity and clarity, leaving hiring managers with little insight into the candidate's strengths or suitability for the position. Generic phrases do not capture attention and may lead to the candidate being overlooked in favor of those with more impactful titles.
Writing an Exceptional Semiconductor Engineer Resume Summary
A well-crafted resume summary is crucial for Semiconductor Engineers looking to make a strong impression on hiring managers. This concise paragraph serves as an introduction that highlights the candidate's key skills, relevant experience, and significant accomplishments, effectively capturing attention in a competitive job market. A compelling summary should be impactful and tailored to the specific job description, allowing recruiters to quickly assess the candidate's suitability for the role and encouraging them to delve deeper into the resume.
Best Practices for Writing a Semiconductor Engineer Resume Summary
- Quantify achievements: Use numbers and metrics to demonstrate your impact in previous roles.
- Focus on relevant skills: Highlight technical skills and competencies that align with the job description.
- Tailor your summary: Customize your summary for each job application to reflect the specific requirements of the role.
- Be concise: Keep your summary to 2-4 sentences to ensure clarity and brevity.
- Use action verbs: Start sentences with powerful action verbs to convey confidence and proactivity.
- Showcase industry knowledge: Include relevant industry terminology and knowledge to highlight your expertise.
- Highlight unique selling points: Identify what sets you apart from other candidates and make that clear in your summary.
- Proofread: Ensure there are no grammatical errors or typos to maintain a professional image.
Example Semiconductor Engineer Resume Summaries
Strong Resume Summaries
Results-driven Semiconductor Engineer with over 5 years of experience in process optimization, leading to a 30% increase in yield rates. Proficient in advanced lithography techniques and CAD tools, with a proven track record in developing innovative solutions to complex engineering challenges.
Detail-oriented Semiconductor Engineer with expertise in VLSI design and simulation, successfully reducing project timelines by 20% through efficient workflow management. Recognized for contributions to a high-profile chip development project that achieved record-breaking performance benchmarks.
Innovative Semiconductor Engineer with a Master’s degree in Electrical Engineering and 7 years of experience in semiconductor fabrication. Improved production efficiency by 25% through the implementation of new quality control protocols and cross-functional team collaboration.
Weak Resume Summaries
Motivated engineer looking for a job in the semiconductor industry. I have some experience and skills that might be useful.
Semiconductor Engineer with a variety of skills and a degree in engineering. I am eager to learn and contribute to a team.
The strong resume summaries are effective because they provide specific details about achievements, quantify results, and align closely with the Semiconductor Engineer role. They present the candidate as a capable professional with proven success. In contrast, the weak summaries are vague, lack measurable outcomes, and do not demonstrate a clear understanding of the job requirements, making them less appealing to hiring managers.
Work Experience Section for Semiconductor Engineer Resume
The work experience section of a Semiconductor Engineer resume plays a vital role in demonstrating the candidate's technical skills and their capacity to manage teams effectively. This section highlights the hands-on experience that is crucial in the semiconductor industry, showcasing the candidate’s ability to deliver high-quality products under tight deadlines. By quantifying achievements and aligning their experience with industry standards, candidates can provide compelling evidence of their contributions to past projects, making them stand out to potential employers.
Best Practices for Semiconductor Engineer Work Experience
- Clearly articulate technical skills relevant to semiconductor design and manufacturing.
- Quantify achievements with specific metrics, such as yield improvements or cost reductions.
- Showcase leadership experience in managing projects or mentoring team members.
- Highlight collaboration with cross-functional teams to demonstrate teamwork and communication skills.
- Use industry-standard terminology and practices to align with the expectations of hiring managers.
- Focus on results-driven narratives that emphasize how your contributions impacted the organization.
- Include any relevant certifications or training that enhances your technical expertise.
- Tailor the work experience section to match the requirements of the job you are applying for.
Example Work Experiences for Semiconductor Engineer
Strong Experiences
- Led a cross-functional team of 10 engineers in the development of a new 7nm process technology, resulting in a 25% increase in chip performance.
- Implemented a yield optimization strategy that improved production efficiency by 30%, saving the company $2 million annually.
- Designed and executed a training program for junior engineers, enhancing their proficiency in semiconductor simulation tools, which accelerated project timelines by 15%.
- Collaborated with the supply chain team to streamline the procurement process, reducing material costs by 20% while maintaining quality standards.
Weak Experiences
- Worked on various semiconductor projects without specific details or outcomes.
- Assisted team members with tasks related to semiconductor engineering.
- Participated in meetings to discuss project updates.
- Gained experience in semiconductor technology over several years.
The examples provided are categorized as strong or weak based on their specificity and impact. Strong experiences include quantifiable outcomes and detailed descriptions of leadership and collaboration, making them compelling to potential employers. In contrast, weak experiences lack measurable achievements and detailed information, making it difficult for hiring managers to gauge the candidate's true value and contributions. A well-structured work experience section should emphasize relevant accomplishments and leadership roles to stand out in the competitive field of semiconductor engineering.
Education and Certifications Section for Semiconductor Engineer Resume
The education and certifications section of a Semiconductor Engineer resume is crucial as it showcases the candidate's academic qualifications, relevant certifications, and commitment to continuous learning in a rapidly evolving industry. This section not only highlights the foundational knowledge gained through formal education but also emphasizes specialized training and industry-recognized credentials that enhance the candidate's credibility. By providing detailed information on relevant coursework and certifications, candidates can effectively demonstrate their alignment with the job role, showcasing their preparedness to tackle the challenges in semiconductor engineering.
Best Practices for Semiconductor Engineer Education and Certifications
- Include degrees relevant to semiconductor engineering, such as Electrical Engineering or Materials Science.
- List industry-recognized certifications, such as Certified Semiconductor Professional (CSP) or Six Sigma Green Belt.
- Highlight specialized training programs or workshops that enhance technical skills relevant to the semiconductor industry.
- Provide details on relevant coursework that demonstrates knowledge in semiconductor physics, fabrication techniques, or circuit design.
- Use clear formatting to distinguish between degrees, certifications, and training for easy readability.
- Update the section regularly to include any new certifications or relevant educational pursuits.
- Prioritize certifications and courses that are in high demand or specific to the job description.
- Consider including any honors or awards received during your academic career to further enhance credibility.
Example Education and Certifications for Semiconductor Engineer
Strong Examples
- B.S. in Electrical Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, 2021
- Certified Semiconductor Professional (CSP), 2022
- Relevant Coursework: Semiconductor Physics, VLSI Design, and Microfabrication Techniques
- Advanced Training in Cleanroom Protocols and Wafer Fabrication, 2023
Weak Examples
- B.A. in English Literature, University of Michigan, 2019
- Certification in Basic Computer Skills, 2020
- Outdated training in Analog Circuit Design, 2015
- High School Diploma, 2015
The strong examples are considered effective as they directly relate to the core competencies required for a Semiconductor Engineer, showcasing relevant degrees and certifications that demonstrate both educational rigor and professional development. In contrast, the weak examples illustrate a lack of relevance to the field, such as degrees and certifications that do not pertain to semiconductor engineering, which could undermine the candidate's suitability for the role.
Top Skills & Keywords for Semiconductor Engineer Resume
In the competitive field of semiconductor engineering, having a well-crafted resume that highlights the right skills is crucial for standing out to potential employers. Skills serve as the foundation of your professional identity, showcasing your technical expertise and interpersonal abilities. A compelling resume not only lists your qualifications but also effectively communicates how your skills align with the demands of the job. This is particularly important in semiconductor engineering, where innovation and precision are paramount. By emphasizing both hard and soft skills, you can demonstrate your capability to contribute to cutting-edge projects and collaborate effectively within multidisciplinary teams. For more insights on how to enhance your resume, consider exploring additional resources on skills and work experience.
Top Hard & Soft Skills for Semiconductor Engineer
Hard Skills
- Semiconductor Device Physics
- Circuit Design and Analysis
- VLSI Design and Layout
- Process Technology Knowledge
- Schematic Capture and PCB Design
- Test and Measurement Equipment Proficiency
- CAD Software (e.g., Cadence, Mentor Graphics)
- Semiconductor Fabrication Techniques
- Material Science for Semiconductors
- Statistical Process Control (SPC)
- Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Embedded Systems Design
- Failure Analysis Techniques
- Cleanroom Protocols
- RF and Microwave Engineering
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
- Programming Languages (e.g., Python, C++)
Soft Skills
- Strong Problem-Solving Abilities
- Effective Communication Skills
- Team Collaboration and Leadership
- Time Management and Organization
- Attention to Detail
- Adaptability and Flexibility
- Critical Thinking
- Creativity and Innovation
- Project Management
- Conflict Resolution
- Initiative and Proactiveness
- Customer Focus
- Analytical Thinking
- Mentoring and Training Others
- Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity
- Networking and Relationship Building
- Resilience and Stress Management
Stand Out with a Winning Semiconductor Engineer Cover Letter
Dear [Hiring Manager's Name],
I am writing to express my interest in the Semiconductor Engineer position at [Company Name], as advertised on [Where You Found the Job Posting]. With a solid background in semiconductor design and manufacturing, coupled with my hands-on experience in advanced materials and process engineering, I am excited about the opportunity to contribute to your innovative projects. My academic qualifications include a Master’s degree in Electrical Engineering from [University Name], where I specialized in semiconductor device fabrication and characterization.
In my previous role at [Previous Company Name], I was responsible for optimizing production processes for advanced semiconductor devices, which led to a 15% increase in yield and a significant reduction in processing time. I have a thorough understanding of cleanroom protocols and have collaborated closely with cross-functional teams to troubleshoot fabrication issues and implement effective solutions. Additionally, my experience with simulation tools such as Cadence and ANSYS has enabled me to design and evaluate complex circuits effectively, ensuring they meet both performance and reliability standards.
I am particularly impressed by [Company Name]'s commitment to sustainability and innovation in semiconductor technology. I am eager to bring my expertise in developing energy-efficient devices and my passion for cutting-edge research to your team. I am confident that my proactive approach to problem-solving and my strong communication skills will allow me to collaborate effectively with engineers and researchers to drive successful outcomes.
Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the opportunity to discuss how my skills and experiences align with the goals of [Company Name]. I am excited about the prospect of contributing to your team and am available at your earliest convenience for an interview.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
[Your LinkedIn Profile or Contact Information]
Common Mistakes to Avoid in a Semiconductor Engineer Resume
When crafting a resume as a Semiconductor Engineer, it is crucial to present your skills and experience effectively to stand out in this competitive field. However, many candidates make common errors that can undermine their chances of landing an interview. Understanding these pitfalls can help you create a more compelling and professional resume that highlights your qualifications and experiences relevant to semiconductor engineering.
Vague Job Descriptions: Failing to provide specific details about your responsibilities and achievements can leave hiring managers unclear about your expertise. Use quantifiable metrics and specific technologies you worked with.
Ignoring Relevant Skills: Listing skills that are not directly relevant to semiconductor engineering can dilute your resume. Focus on specialized skills such as circuit design, semiconductor fabrication, or software tools like CAD.
Lack of Tailoring: Submitting a generic resume that doesn't align with the job description can be a major mistake. Tailor your resume for each position, emphasizing the most relevant experience and skills.
Overly Technical Language: While technical knowledge is essential, using overly complex jargon can alienate non-technical hiring managers. Strive for clarity and balance technical terms with explanations.
Neglecting Soft Skills: Overemphasizing technical skills while ignoring soft skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving can present an incomplete picture. Highlight your ability to collaborate on projects and communicate effectively.
Formatting Issues: A cluttered or poorly organized resume can be difficult to read. Use clear headings, bullet points, and a consistent format to enhance readability and professionalism.
Omitting Certifications or Continuing Education: Failing to include relevant certifications or ongoing education can make your resume less competitive. Ensure that you list any industry-specific certifications or courses that enhance your qualifications.
Not Including Publications or Patents: In a field like semiconductor engineering, research contributions can set you apart. If applicable, include any publications, patents, or significant projects that showcase your expertise and innovation.
Conclusion
As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve, the role of a Semiconductor Engineer remains pivotal in driving innovation and efficiency. Throughout this article, we've explored the essential skills and qualifications that are crucial for success in this field, including expertise in semiconductor physics, proficiency in design software, and the ability to collaborate effectively within multidisciplinary teams.
In addition, we highlighted the importance of staying updated with the latest technological advancements and industry trends, as well as the need for strong problem-solving and analytical skills. With the demand for semiconductor engineers on the rise, having a standout resume is more important than ever.
Now is the perfect time to review and enhance your Semiconductor Engineer resume to ensure it effectively showcases your skills and experiences. To assist you in this process, we encourage you to take advantage of the following resources:
- Explore a variety of resume templates that can help you structure your information professionally.
- Use our intuitive resume builder to create a customized resume that highlights your unique qualifications.
- Check out resume examples for inspiration and guidance on how to present your achievements.
- Don’t forget to craft a compelling cover letter with the help of our cover letter templates to make a strong impression on potential employers.
Take action today and ensure your resume reflects your qualifications and readiness to excel in the semiconductor engineering field!